Welcome to Facts Vibes! Today, we’re delving into fascinating fun facts about the Ring of Fire. From volcanic eruptions to seismic activity, this renowned region encircling the Pacific Ocean is packed with geological marvels. Join us as we uncover the captivating secrets of this fiery expanse.
The Ring of Fire: A Fascinating Geological Phenomenon
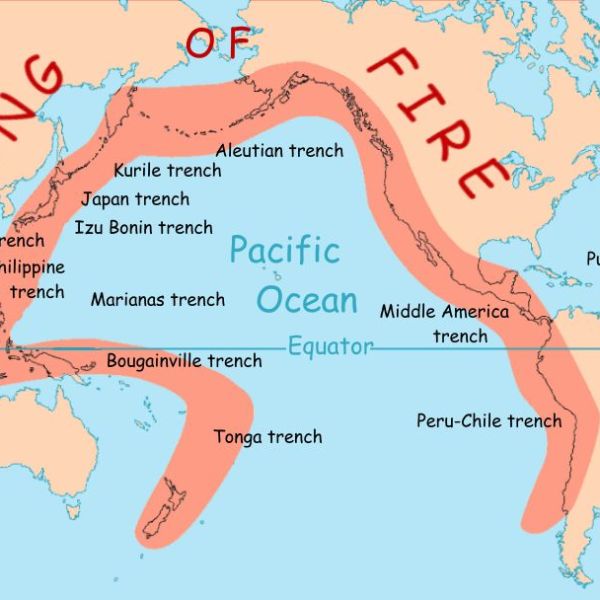
The Ring of Fire is a fascinating geological phenomenon that encompasses a vast area in the Pacific Ocean. It is characterized by a string of volcanoes, earthquake zones, and tectonic plate movements. This region is named the Ring of Fire due to the high levels of tectonic activity that generate frequent earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. The *Pacific Ring of Fire* stretches approximately 25,000 miles and is home to about 75% of the world’s active and dormant volcanoes. The tectonic activity in this area is mainly caused by the movement and collisions of several tectonic plates, leading to the creation of various volcanic arcs and oceanic trenches. The geological processes at work in the Ring of Fire continue to captivate scientists and researchers, providing valuable insights into earth sciences and natural hazards.
Most popular facts
The Ring of Fire is a horseshoe-shaped area in the Pacific Ocean known for intense seismic and volcanic activity.
The Ring of Fire is a horseshoe-shaped area in the Pacific Ocean known for intense seismic and volcanic activity.
It spans approximately 25,000 miles and encompasses 452 volcanoes.
The answer to that question is that it spans approximately 25,000 miles and encompasses 452 volcanoes.
The region is home to about 75% of the world’s active and dormant volcanoes.
The region is home to about 75% of the world’s active and dormant volcanoes.
More than half of the world’s earthquakes occur within the Ring of Fire.
True.
The Ring of Fire is responsible for 90% of the world’s earthquakes over
Sure! The Ring of Fire is responsible for 90% of the world’s earthquakes.
0 magnitude.
In the context of Information and facts, magnitude refers to the size or extent of a particular phenomenon or data point.
Major tectonic plates, including the Pacific Plate, North American Plate, and Eurasian Plate, intersect within the Ring of Fire.
The Ring of Fire is where major tectonic plates, including the Pacific Plate, North American Plate, and Eurasian Plate, intersect.
The 2011 Tohoku earthquake in Japan, which triggered a devastating tsunami, occurred within the Ring of Fire.
True.
Over 22,000 people have died in the past 400 years due to volcanic eruptions within the Ring of Fire.
Over 22,000 people have died in the past 400 years due to volcanic eruptions within the Ring of Fire.
The 1883 eruption of Krakatoa, located within the Ring of Fire, was one of the most powerful volcanic events in recorded history.
The 1883 eruption of Krakatoa, located within the Ring of Fire, was one of the most powerful volcanic events in recorded history.
The Ring of Fire hosts several active submarine volcanoes, contributing to the geological dynamics of the region.
The Ring of Fire hosts several active submarine volcanoes, contributing to the geological dynamics of the region.
The Pacific Northwest of the United States, part of the Ring of Fire, faces potential risks from the Cascadia Subduction Zone.
The Pacific Northwest of the United States, part of the Ring of Fire, faces potential risks from the Cascadia Subduction Zone.
The Aleutian Islands in Alaska are a prominent part of the Ring of Fire and host numerous active volcanoes.
The Aleutian Islands in Alaska are a prominent part of the Ring of Fire and host numerous active volcanoes.
The Ring of Fire influences the climate and biodiversity of the surrounding regions due to its volcanic and seismic activity.
In addition to Japan and the United States, the Ring of Fire impacts countries such as Indonesia, the Philippines, and Chile.
The Ring of Fire impacts countries such as Indonesia, the Philippines, and Chile, in addition to Japan and the United States.
The Ring of Fire is constantly monitored by scientists and researchers to better understand and predict volcanic and seismic events.
The Ring of Fire is constantly monitored by scientists and researchers to better understand and predict volcanic and seismic events.
In conclusion, the Ring of Fire serves as a captivating reminder of the Earth’s dynamic and ever-changing nature. Its fascinating geological features and the impact on the environment are a testament to the power and beauty of our planet. Exploring the Ring of Fire not only provides a deeper understanding of natural phenomena, but also underscores the importance of preparedness and resilience in the face of potential geological hazards.