Sure, here’s the introduction:
“Welcome to Facts Vibes! Today, we’re diving into the intriguing Caspian Sea facts. From its unique status as the world’s largest enclosed body of water to its rich biodiversity, join us as we explore the wonders of this enigmatic sea.”
Caspian Sea: A Treasure Trove of Fascinating Facts
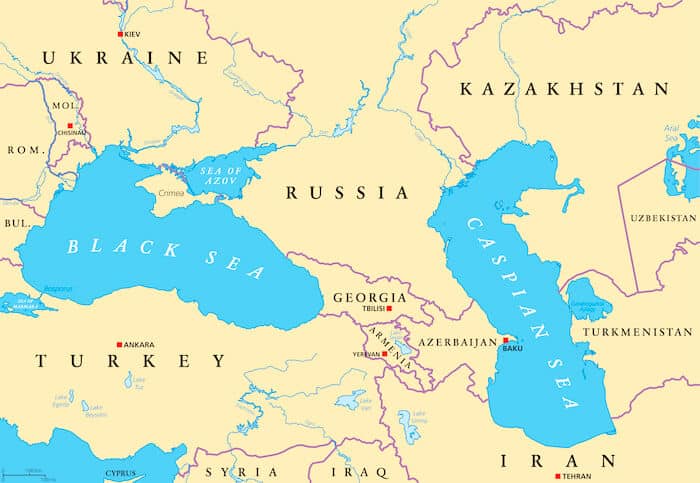
The Caspian Sea is the largest enclosed inland body of water on Earth, encompassing an incredible surface area of 371,000 square kilometers. It borders five countries, including Russia, Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan, Iran, and Azerbaijan, and its diverse ecosystems are home to a wide variety of flora and fauna. The Caspian Sea also holds significant oil and gas reserves, contributing to its economic importance in the region. Furthermore, it has a fascinating geological history, having formed around 5.5 million years ago. The Caspian Sea has been essential for trade and transportation throughout history and continues to play a crucial role in the global economy today. Its unique characteristics make it a treasure trove of natural beauty and resources, attracting researchers, tourists, and those interested in its rich cultural heritage.
Most popular facts
The Caspian Sea is the world’s largest inland body of water, covering an area of 371,000 square kilometers.
The Caspian Sea is the world’s largest inland body of water, covering an area of 371,000 square kilometers.
It is bordered by five countries: Russia, Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan, Iran, and Azerbaijan.
It is bordered by five countries: Russia, Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan, Iran, and Azerbaijan.
The sea is saline, with salinity levels varying from brackish to nearly three times that of the ocean.
The sea has saline water, with salinity levels ranging from brackish to nearly three times that of the ocean.
Sturgeon, the source of caviar, is found in the Caspian Sea and has been a major part of its ecosystem and economy.
Sturgeon, the source of caviar, is found in the Caspian Sea and has been a major part of its ecosystem and economy.
The Volga River, Europe’s longest river, is the main source of freshwater inflow into the Caspian Sea.
The Volga River is the main source of freshwater inflow into the Caspian Sea.
The sea is home to unique species of flora and fauna, some of which are not found anywhere else in the world.
The sea is home to unique species of flora and fauna, some of which are not found anywhere else in the world.
Oil and natural gas reserves in the Caspian Sea region are significant, making it a strategically important area for energy production.
The oil and natural gas reserves in the Caspian Sea region are significant, making it a strategically important area for energy production.
The Caspian Sea has experienced fluctuations in water level over time, impacting its surrounding ecosystems and human settlements.
The Caspian Sea has experienced fluctuations in water level over time, impacting its surrounding ecosystems and human settlements.
Major ports and cities, such as Baku and Astrakhan, are situated along the Caspian Sea’s coastline, contributing to regional trade and commerce.
Baku and Astrakhan are major ports and cities situated along the coastline of the Caspian Sea, contributing significantly to regional trade and commerce.
The sea has historically been an important cultural and economic crossroads, with diverse influences from Persian, Turkic, and Russian civilizations.
The sea has historically been an important cultural and economic crossroads, with diverse influences from Persian, Turkic, and Russian civilizations.
Caspian seals, the only marine mammals endemic to the Caspian Sea, are currently listed as endangered due to habitat degradation and overfishing.
The Caspian seals are currently listed as endangered due to habitat degradation and overfishing.
The sea’s strategic location has made it a focus of geopolitical interests and disputes among the surrounding countries.
The sea’s strategic location has made it a focus of geopolitical interests and disputes among the surrounding countries.
The construction of dams and water diversions from rivers feeding into the Caspian Sea has impacted its water balance and ecological health.
The construction of dams and water diversions from rivers feeding into the Caspian Sea has impacted its water balance and ecological health.
The Caspian Sea has long served as a vital transportation route, connecting regions and facilitating trade between Europe and Asia.
The Caspian Sea has long served as a vital transportation route, connecting regions and facilitating trade between Europe and Asia.
Climate change and environmental degradation pose significant challenges to the Caspian Sea’s long-term sustainability and ecological balance.
Climate change and environmental degradation are significant challenges to the Caspian Sea’s long-term sustainability and ecological balance.
In conclusion, the Caspian Sea is a remarkable body of water with a unique combination of geological, ecological, and geopolitical significance. Its diverse marine life and rich history make it a fascinating area of study for scientists, environmentalists, and historians alike. As the largest enclosed inland body of water on Earth, the Caspian Sea continues to play a crucial role in global trade, energy production, and geopolitical dynamics. Understanding its complexities and protecting its delicate ecosystem is essential for the sustainable future of this extraordinary natural wonder.