Welcome to Facts Vibes! Get ready to dive into the fascinating world of black holes. From mind-boggling theories to mind-blowing discoveries, we’ve rounded up 30 interesting facts about black holes that will leave you in awe. Buckle up for a journey through the extraordinary mysteries of these enigmatic cosmic phenomena.
Unveiling the mysteries of black holes: 30 fascinating facts
Unveiling the mysteries of black holes: 30 fascinating facts in the context of {theme}.
1. Black holes are created when massive stars collapse under their own gravity.
2. The gravitational pull of a black hole is so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape from it.
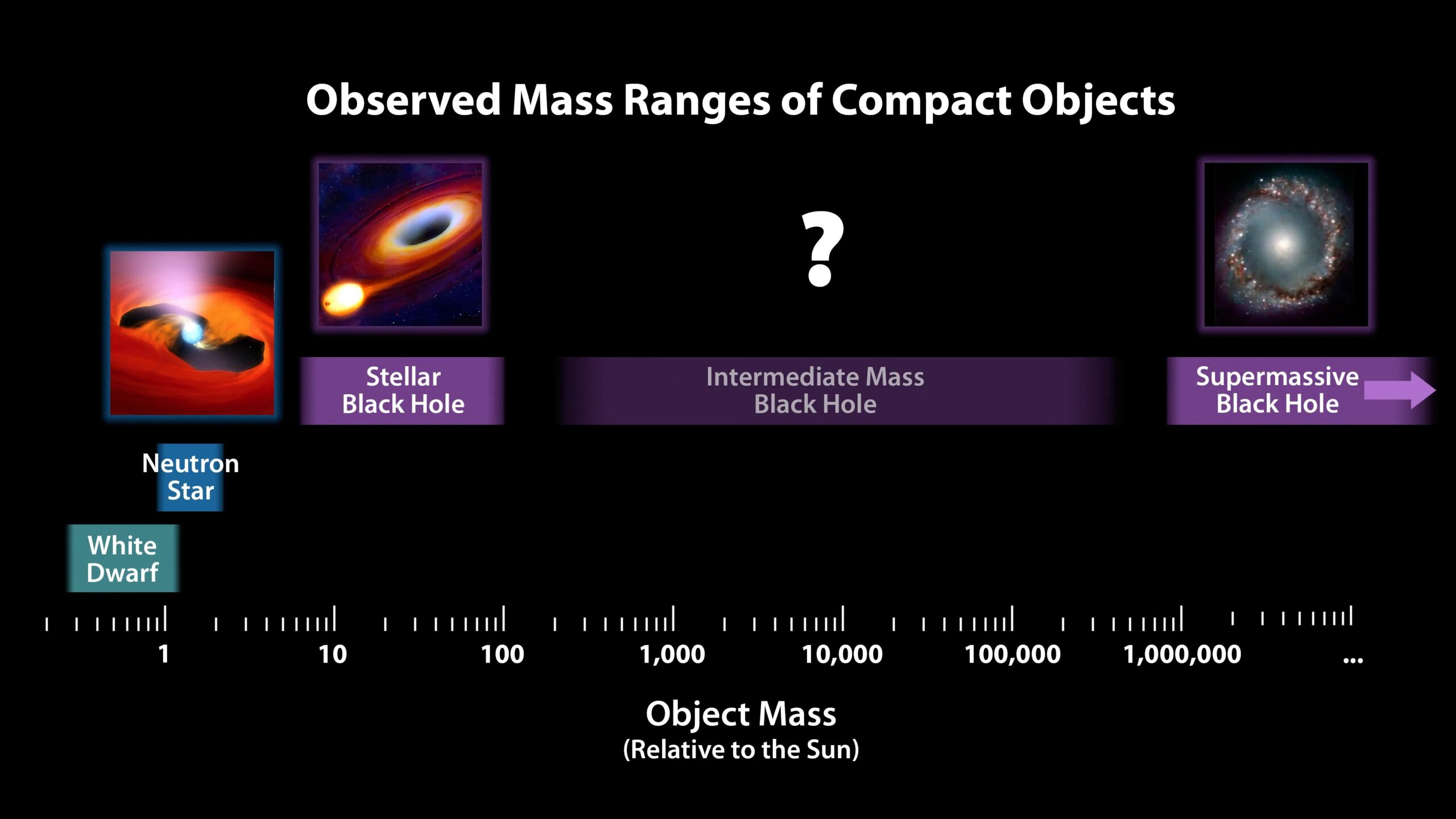
3. Black holes come in different sizes, from small ones created by single stars to supermassive ones found at the center of galaxies.
4. The boundary surrounding a black hole from which no light or matter can escape is called the event horizon.
5. Despite their name, black holes are not empty but rather contain a huge amount of mass squeezed into a tiny space.
6. The first image of a black hole was captured in 2019 by the Event Horizon Telescope, revealing the shadow of the black hole at the center of the galaxy M87.
7. Stephen Hawking proposed that black holes emit radiation, now known as Hawking radiation, and can eventually evaporate and disappear.
8. Black holes can distort time and space, a phenomenon described by Einstein’s theory of general relativity.
9. There is a hypothesis that suggests black holes could be portals to other parts of the universe or even different universes altogether.
10. The study of black holes has led to advancements in our understanding of fundamental physics and the nature of spacetime.
11. The word “black hole” was coined by physicist John Archibald Wheeler in 1967.
12. Some black holes are in binary systems, where they orbit around a companion star and can siphon off material from it.
13. Black holes can also be detected by the gravitational waves they produce when they merge with another black hole or neutron star.
14. The nearest known black hole to Earth is located in the constellation of Vela and is about 1,000 light-years away.
15. In the center of the Milky Way, there is a supermassive black hole named Sagittarius A*.
16. The existence of black holes was predicted by the equations of general relativity long before they were observed directly.
17. Astronomers think there could be millions or even billions of black holes in our galaxy alone.
18. Scientists are still trying to understand what happens to information that falls into a black hole, as it challenges the principles of quantum mechanics.
19. Black holes can be “fed” by surrounding matter, causing them to grow in mass and size over time.
20. The study of black holes continues to be a crucial area of research in astrophysics and cosmology.
21. Some black holes spin at incredibly high speeds, creating a dragging effect on spacetime called frame-dragging.
22. The extreme conditions near a black hole can cause the emission of powerful jets of particles traveling close to the speed of light.
23. The term “singularity” is used to describe the infinitely dense and hot point within a black hole.
24. The process of stars collapsing into black holes is a vital part of the cycle of stellar evolution.
25. Black holes can have a profound impact on the surrounding galaxies by influencing star formation and distribution.
26. The potential connection between black holes and dark matter remains an intriguing topic for scientific exploration.
27. The study of black holes has expanded our knowledge of the universe’s history and evolution.
28. It is theorized that smaller black holes could be more common than larger ones and may even exist as remnants of the early universe.
29. Understanding black holes could provide insight into the behavior of matter and energy under extreme conditions.
30. New observations and theoretical advances continue to deepen our understanding of black holes and their role in shaping the cosmos.
Most popular facts
Black holes are regions in space where the gravitational pull is so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape from them.
Black holes are regions in space where the gravitational pull is so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape from them.
The gravity near a black hole is so powerful that it distorts and stretches anything that comes close to it.
The gravity near a black hole is so powerful that it distorts and stretches anything that comes close to it.
Black holes come in different sizes, with the smallest ones being called “stellar black holes.”
Sure! Black holes come in different sizes, with the smallest ones being called “stellar black holes.”
Supermassive black holes, found at the centers of galaxies, can have masses equivalent to millions or billions of suns.
Supermassive black holes, found at the centers of galaxies, can have masses equivalent to millions or billions of suns.
The concept of black holes was first introduced by physicist John Michell in 1783 and later popularized by Albert Einstein’s theory of general relativity.
The concept of black holes was first introduced by physicist John Michell in 1783 and later popularized by Albert Einstein’s theory of general relativity.
The boundary surrounding a black hole, beyond which nothing can escape, is called the event horizon.
The boundary surrounding a black hole, beyond which nothing can escape, is called the event horizon.
Despite their name, black holes are not actually empty but are incredibly dense with a high concentration of matter.
Black holes are not actually empty but are incredibly dense with a high concentration of matter.
Black holes can be detected indirectly through their gravitational influence on nearby objects and the radiation they emit.
Black holes can be detected indirectly through their gravitational influence on nearby objects and the radiation they emit.
The intense gravitational forces near a black hole can cause time to slow down, a phenomenon known as time dilation.
Black holes can cause time dilation due to the intense gravitational forces near them.
Black holes can merge with each other, releasing an enormous amount of energy in the form of gravitational waves.
Yes, black holes can merge with each other, releasing an enormous amount of energy in the form of gravitational waves.
The largest known black hole, TON 618, has a mass estimated to be 66 billion times that of the Sun.
The largest known black hole, TON 618, has a mass estimated to be 66 billion times that of the Sun.
Microscopic black holes, also known as primordial black holes, are hypothetical tiny black holes that could have formed in the early universe.
Microscopic black holes, also known as primordial black holes, are hypothetical tiny black holes that could have formed in the early universe.
The study of black holes has led to the development of important concepts in physics, such as Hawking radiation and the information paradox.
The study of black holes has led to the development of important concepts in physics, such as Hawking radiation and the information paradox.
Astronomers have observed evidence of supermassive black holes in the centers of many galaxies, including our own Milky Way.
Astronomers have observed evidence of supermassive black holes in the centers of many galaxies, including our own Milky Way.
There are ongoing efforts to capture the first-ever direct image of a black hole using a global network of telescopes known as the Event Horizon Telescope.
Efforts are ongoing to capture the first-ever direct image of a black hole using a global network of telescopes known as the Event Horizon Telescope.
In conclusion, black holes continue to captivate and intrigue scientists and space enthusiasts alike. Their mysterious nature and immense power make them a fascinating topic of study and exploration. These 30 facts about black holes shed light on their extraordinary properties and the important role they play in shaping the universe. From their formation to their potential contribution to scientific breakthroughs, black holes are a constant source of wonder and discovery in the field of astrophysics.