Welcome to Facts Vibes! Delve into the fascinating world of geology as we explore 10 captivating facts about the layers of the Earth. Uncover the secrets beneath our feet and gain a deeper understanding of the incredible forces at work within our planet.
The Fascinating Layers of the Earth: 10 Intriguing Facts
The Earth is a complex and wondrous planet, with many layers that hold intricate secrets about its formation and composition. Here are 10 intriguing facts about the fascinating layers of the Earth:
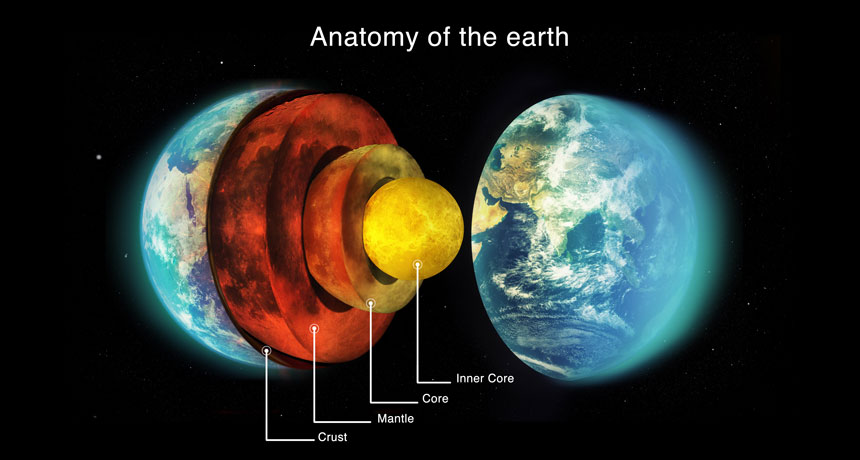
1. The Earth’s crust is the outermost layer and is divided into several large and small tectonic plates.
2. The mantle lies beneath the crust and is made up of solid rock that can flow over long periods of time.
3. The outer core is composed of liquid iron and nickel, creating the Earth’s magnetic field.
4. At the center of the Earth lies the inner core, a solid ball of iron and nickel that is hotter than the surface of the sun.
5. The movement of the tectonic plates creates earthquakes, volcanic activity, and mountain formation.
6. Convection currents in the mantle are responsible for moving the tectonic plates.
7. The Earth’s crust is not a continuous layer but is broken into oceanic crust and continental crust.
8. The layer known as Asthenosphere allows the movement of the tectonic plates due to its semi-fluid nature.
9. There are various methods, such as seismic waves and drilling, used to study the layers of the Earth.
10. Understanding the layers of the Earth is crucial for understanding geological processes and predicting natural disasters.
The Earth’s layers are a captivating topic that reveals the planet’s dynamic nature and history.
Most popular facts
The Earth’s layers are divided into the crust, mantle, outer core, and inner core.
The Earth’s layers are divided into the crust, mantle, outer core, and inner core.
The Earth’s crust is composed of solid rock and is the thinnest layer, ranging from 5 to 70 kilometers thick.
The Earth’s crust is composed of solid rock and is the thinnest layer, ranging from 5 to 70 kilometers thick.
The mantle is the thickest layer, accounting for about 84% of the Earth’s total volume.
The mantle is the thickest layer, accounting for about 84% of the Earth’s total volume.
The outer core is made of liquid iron and nickel, and it is responsible for generating the Earth’s magnetic field.
The outer core is made of liquid iron and nickel, and it is responsible for generating the Earth’s magnetic field.
The inner core is primarily made of solid iron and nickel, with temperatures reaching over 5,000 degrees Celsius.
The inner core is primarily made of solid iron and nickel, with temperatures reaching over 5,000 degrees Celsius.
The boundary between the crust and mantle is known as the Mohorovičić discontinuity (Moho).
The boundary between the crust and mantle is known as the Mohorovičić discontinuity (Moho).
The lithosphere, which includes the crust and uppermost part of the mantle, is divided into tectonic plates that move and interact with each other.
The lithosphere, including the crust and uppermost part of the mantle, is divided into tectonic plates that move and interact with each other.
The asthenosphere, a semi-fluid layer beneath the lithosphere, plays a crucial role in plate tectonics and the movement of the Earth’s surface.
The asthenosphere is a semi-fluid layer beneath the lithosphere that plays a crucial role in plate tectonics and the movement of the Earth’s surface.
The lower mantle experiences high pressures and temperatures, causing it to behave like a solid over long periods of time.
The lower mantle experiences high pressures and temperatures, causing it to behave like a solid over long periods of time.
The discovery of seismic waves and their behavior led to our understanding of the Earth’s layers and composition.
The discovery of seismic waves and their behavior led to our understanding of the Earth’s layers and composition.
Rocks in the Earth’s crust provide valuable information about the planet’s history and evolution.
Rocks in the Earth’s crust are valuable sources of information about the planet’s history and evolution.
The Earth’s layers are constantly in motion, driven by convection currents and heat from the planet’s interior.
The Earth’s layers are constantly in motion, driven by convection currents and heat from the planet’s interior.
The study of the Earth’s layers and their properties helps scientists understand natural phenomena such as earthquakes and volcanic activity.
The study of the Earth’s layers and their properties helps scientists understand natural phenomena such as earthquakes and volcanic activity.
The composition and properties of the Earth’s layers have a significant impact on the planet’s surface features and ecosystems.
The composition and properties of the Earth’s layers directly influence the planet’s surface features and ecosystems.
Understanding the Earth’s layers is essential for various scientific disciplines, including geology, seismology, and geophysics.
Understanding the Earth’s layers is essential for various scientific disciplines, including geology, seismology, and geophysics in the context of Information and facts.
In conclusion, the layers of the Earth are a fascinating study that offers insight into the complex and dynamic nature of our planet. From the solid inner core to the diverse composition of the crust, the Earth’s layers play a crucial role in shaping the world we live in. Understanding these geological formations can help us comprehend natural phenomena, geological events, and even the potential for resource exploration and preservation. As we continue to delve deeper into the mysteries of Earth’s interior, we gain a better appreciation for the intricacies of our planet and its enduring impact on the environment and life.